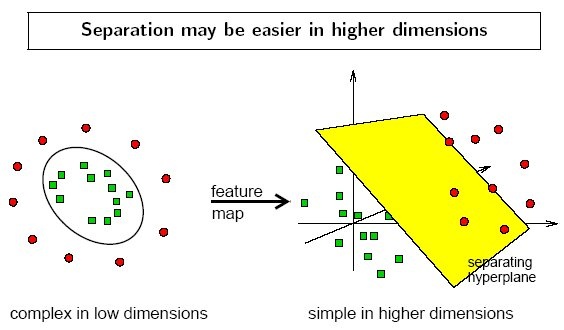
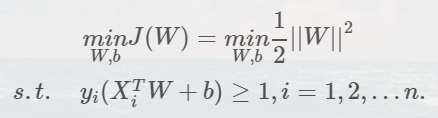1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
| from __future__ import print_function
from time import time
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_people
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCA
from sklearn.svm import SVC
print(__doc__)
# Display progress logs on stdout
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')
###############################################################################
# Download the data, if not already on disk and load it as numpy arrays
lfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4) #下载人脸
# introspect the images arrays to find the shapes (for plotting)
n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape
# for machine learning we use the 2 data directly (as relative pixel
# positions info is ignored by this model)
X = lfw_people.data # 特征向量
n_features = X.shape[1] #有多少列
# the label to predict is the id of the person
y = lfw_people.target # 类
target_names = lfw_people.target_names # 所挑选的图片的人名
n_classes = target_names.shape[0] # 有多少行
print("Total dataset size:")
print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)
print("n_features: %d" % n_features)
print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)
###############################################################################
# Split into a training set and a test set using a stratified k fold
# split into a training and testing set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25)
# train_test_split把实例分成训练集和测试集
###############################################################################
# Compute a PCA (eigenfaces) on the face dataset (treated as unlabeled
# dataset): unsupervised feature extraction / dimensionality reduction
n_components = 150
print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"
% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))
t0 = time()
pca = RandomizedPCA(n_components=n_components, whiten=True).fit(X_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) # RandomizedPCA使用来降维的,因为这个维度抬高难以计算
eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components, h, w))
print("Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis")
t0 = time()
X_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train)
X_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
###############################################################################
# Train a SVM classification model
print("Fitting the classifier to the training set")
t0 = time()
param_grid = {'C': [1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5],
'gamma': [0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.1], }
clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='auto'), param_grid)#核函数kernel, GridSearchCV是用来寻找最好的参数比例
clf = clf.fit(X_train_pca, y_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print("Best estimator found by grid search:")
print(clf.best_estimator_)
###############################################################################
# Quantitative evaluation of the model quality on the test set
print("Predicting people's names on the test set")
t0 = time()
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test_pca)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=target_names))
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=range(n_classes)))
###############################################################################
# Qualitative evaluation of the predictions using matplotlib
def plot_gallery(images, titles, h, w, n_row=3, n_col=4):
"""Helper function to plot a gallery of portraits"""
plt.figure(figsize=(1.8 * n_col, 2.4 * n_row))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=.01, right=.99, top=.90, hspace=.35)
for i in range(n_row * n_col):
plt.subplot(n_row, n_col, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h, w)), cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(titles[i], size=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
# plot the result of the prediction on a portion of the test set
def title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i):
pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
return 'predicted: %s\ntrue: %s' % (pred_name, true_name)
prediction_titles = [title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i)
for i in range(y_pred.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(X_test, prediction_titles, h, w)
# plot the gallery of the most significative eigenfaces
eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d" % i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(eigenfaces, eigenface_titles, h, w)
plt.show()
|
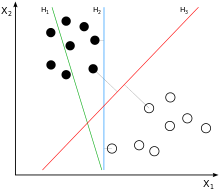
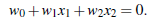 这是二维的,b也就是w0.
这是二维的,b也就是w0.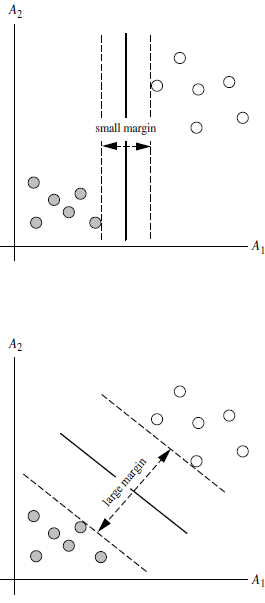
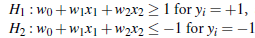
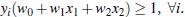 两个公式可以合并
两个公式可以合并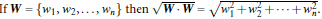 也就是先平方再开方
也就是先平方再开方